
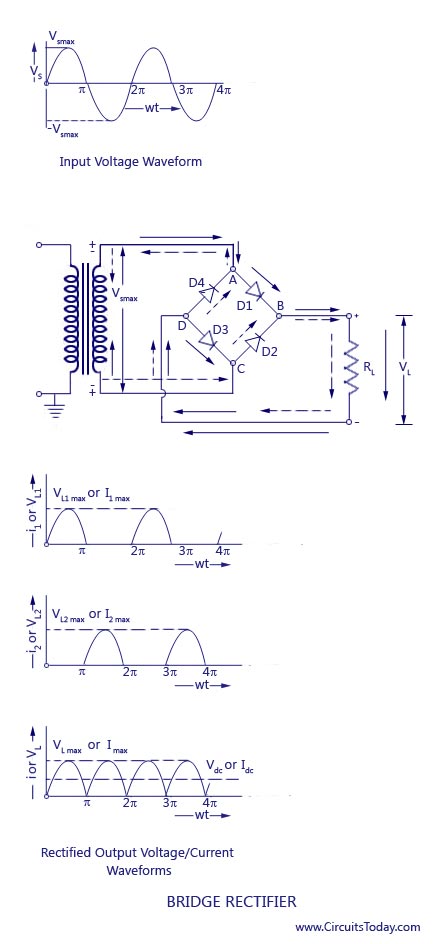

Full wave rectifiers have some fundamental advantages over their half wave rectifier counterparts. Like the half wave circuit, a full wave rectifier circuit produces an output voltage or current which is purely DC or has some specified DC component. The circuit which allows us to do this is called a Full Wave Rectifier. One method to improve on this is to use every half-cycle of the input voltage instead of every other half-cycle. While this method may be suitable for low power applications it is unsuitable to applications which need a “steady and smooth” DC supply voltage.
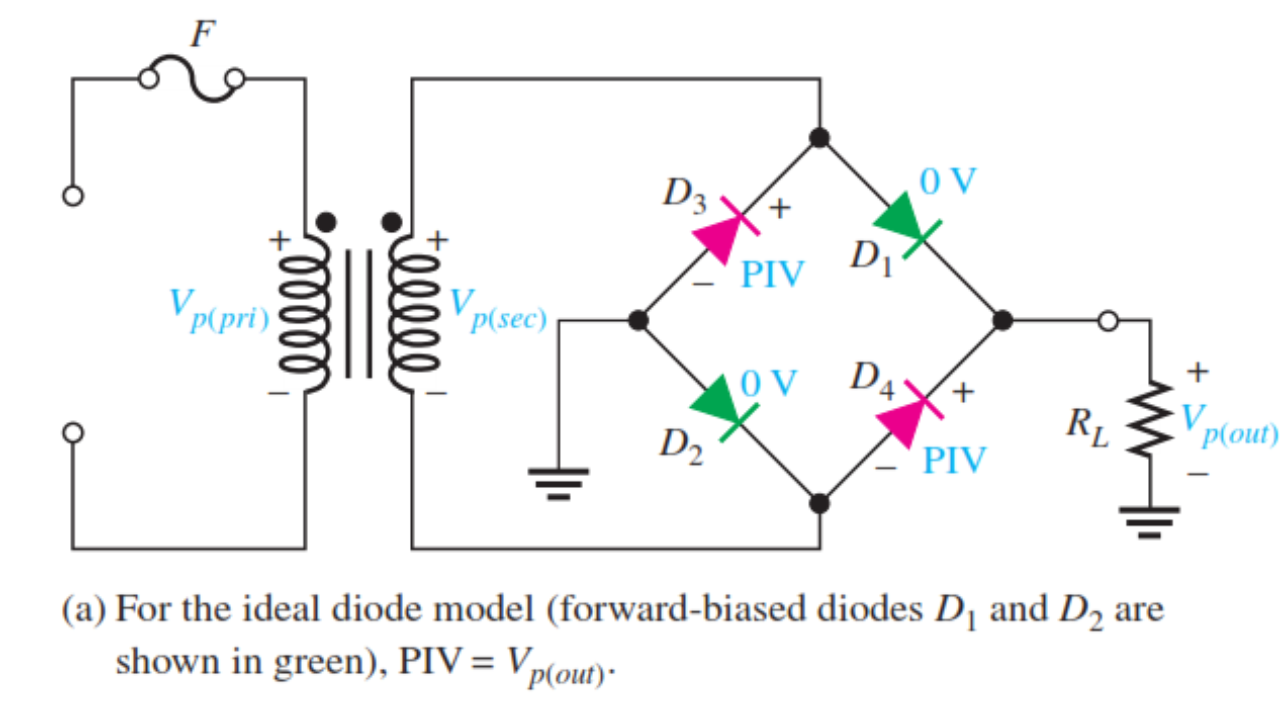
In the previous Power Diodes tutorial we discussed ways of reducing the ripple or voltage variations on a direct DC voltage by connecting smoothing capacitors across the load resistance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
